
Transistor switches from active to reverse active state by swapping the emitter and collector. The collector-emitter current is mostly determined by the base current, which is used to manage the enormous currents flowing through the emitter and collector. Most transistors have a high common-emitter current gain for amplification, which shows the exact current and power gain required for amplification. The collector-base junction is reverse biased, while the emitter-base junction is forward biased. The emitter-base junction and the collector-base junction are the two types of junctions found in BJTs. Working of a Bipolar Junction TransistorīJT has different regions of operation. Conduction current produced by the movement of electrons is deemed rapid and has more value than conduction current produced by the movement of holes, hence this transistor is rarely employed for applications.įigure 1: (a) Types of Bipolar Junction Transistors (n-p-n and p-n-p) and their device symbols (b) Three basic configurations of BJTs namely common base, common collector and common emitter. PNP transistors act similarly to NPN transistors, with the exception that holes from the emitter are diffused through the base and collected by the collector. When compared to NPN transistors, the current and voltage polarities of PNP transistors are reversed. To regulate a big current at the emitter and collector sides, the base utilizes a lower base current and a negative base voltage, and the voltage at the collector side is greater than the voltage at the base side. The PNP (positive-negative-positive) transistor is a form of BJT in which a base layer of N doped semiconductor is sandwiched between two layers of P doped material. On the base side, electrons operate as a minority carrier while the current flows from an emitter to a collector. The base of the transistors is represented by the P doped region, while the emitter and collector are represented by the other two layers.īecause minority charge carriers on the base side are utilized to control significant current at the transistor’s other terminals, NPN transistors are also known as minority carrier devices. The BJTs can be divided into two typesĪ P-doped layer of semiconductor exists between the two layers of n-doped material in an NPN (negative-positive-negative) BJT. Types of BJTsīJTs are classified into two groups based on their nature and structure as shown in Fig. In the base area, electrons act as a minority carrier if the transistor we take is of n-p-n configuration (discussed in the next section). In the base region, the number of electrons diffused is greater than the number of holes diffused in the emitter region.
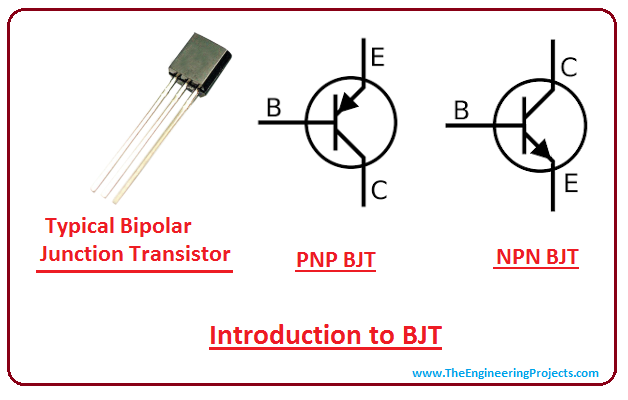
It is a bipolar device in which both charge carriers, namely electrons and holes, conduct. NPN transistors and PNP transistors are the two varieties of BJTs. The collector-base junction is reverse biased, while the emitter-base junction is forward biased.īJTs were originally built of germanium, but more contemporary transistors are made of silicon. The emitter-base junction is a PN junction that exists between the emitter and the base, while the collector-base junction is a PN junction that exists between the collector and the base. This junction stops further diffusion of electrons and holes. Due to the diffusion of holes from the p-type region and diffusion of electrons from the n-type region to the p-side, an electrostatic region of just charges is left at the junction where p-type and n-type materials are joined.

A PN junction is formed when n-type and p-type materials are joined together. There are two PN junctions in this transistor.
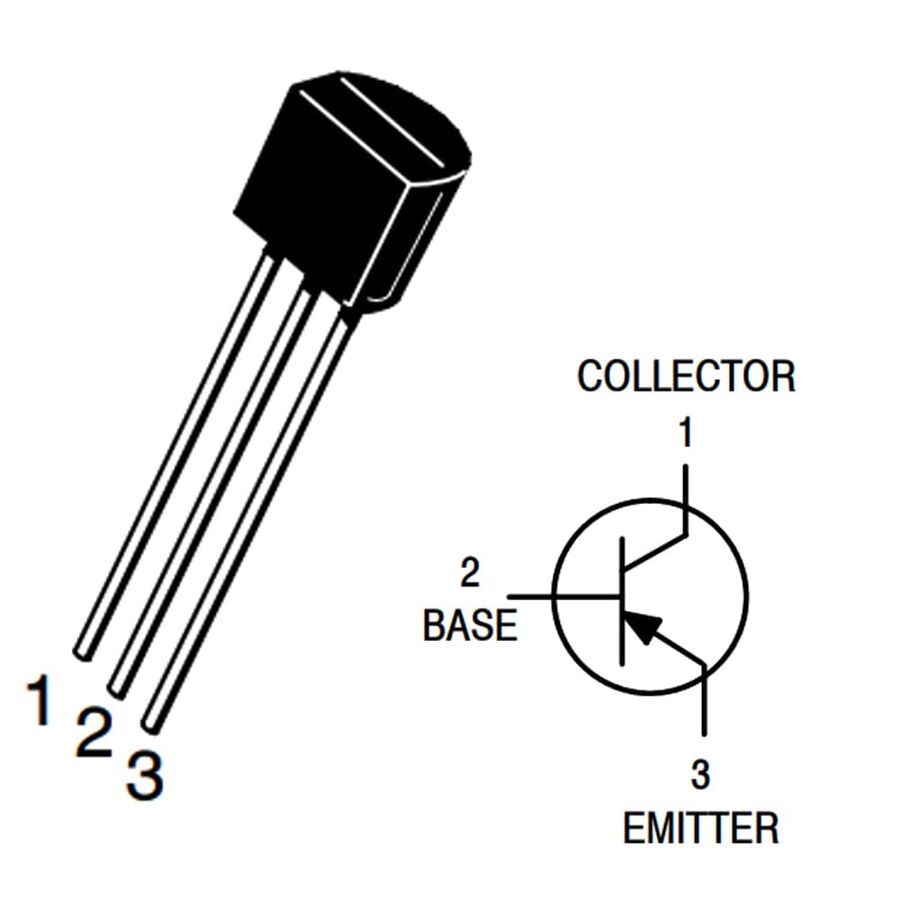
It has three terminals emitter, base, and collector, which are labeled E, B, and C, respectively. Computer memory, microprocessors, and other integrated circuits are built on transistors. The bipolar junction transistor (BJT) was invented in the early 1950s and transformed the world of electronics. Introduction to bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) NPN (a BJT made from n-type, p-type, and n-type semiconductors) and PNP (a BJT made from p-type, n-type, and p-type semiconductors) are the two different types of BJTs that are available in the market. This allows BJTs to be utilized as amplifiers or switches in electronic devices such as cell phones, industrial control, television, and radio transmitters. The primary purpose of a BJT is to amplify the current. The prime objective of this post is to get familiar with bipolar junction transistor (BJT) and its related terminology.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
